Introduction and application of diamond abrasives
Diamond is a substance with the highest hardness in nature. It has extremely high hardness, thermal conductivity and wear resistance, so it is widely used in the abrasive industry. With the development of industrial technology, diamond abrasives have developed from traditional natural diamonds to various artificial diamonds and functional composite materials, becoming an important part of the field of superhard materials, and are widely used in many high-precision industries such as mechanical processing, electronics, optics, and new energy.
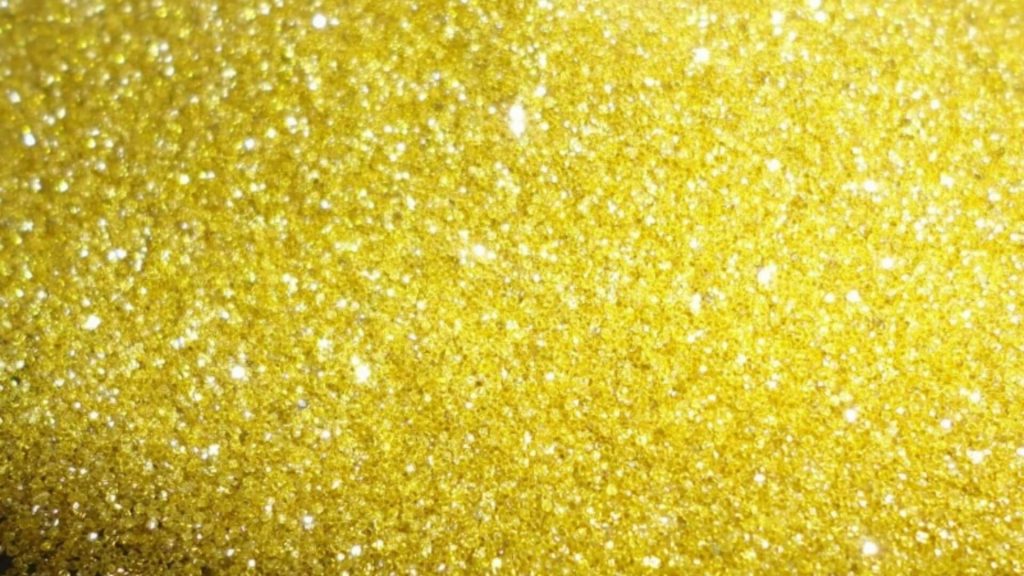 Diamond abrasives are powdered or granular materials made by crushing, screening, and purification of natural diamonds or artificial diamonds. Its Mohs hardness reaches level 10, which is the highest known abrasive. Compared with traditional abrasives such as aluminum oxide and silicon carbide, diamond abrasives have higher cutting ability and wear resistance, and can grind and polish high-hardness materials with high efficiency and low damage.
Diamond abrasives mainly include the following forms:
Diamond micropowder: The particle size ranges from tens of microns to nanometers, suitable for various high-precision polishing processes.
Diamond grinding wheel/grinding head: used for grinding and shaping of hard materials.
Diamond saw blade/drill bit: used for cutting and drilling of materials such as stone, ceramics, glass, etc.
Diamond grinding fluid/polishing paste: widely used in ultra-precision processing in the electronics, optics, mold and other industries.
Composite diamond material (PCD/PCBN): combines diamond with metal or ceramic matrix to form a composite tool material with toughness and wear resistance.
Diamond abrasives are powdered or granular materials made by crushing, screening, and purification of natural diamonds or artificial diamonds. Its Mohs hardness reaches level 10, which is the highest known abrasive. Compared with traditional abrasives such as aluminum oxide and silicon carbide, diamond abrasives have higher cutting ability and wear resistance, and can grind and polish high-hardness materials with high efficiency and low damage.
Diamond abrasives mainly include the following forms:
Diamond micropowder: The particle size ranges from tens of microns to nanometers, suitable for various high-precision polishing processes.
Diamond grinding wheel/grinding head: used for grinding and shaping of hard materials.
Diamond saw blade/drill bit: used for cutting and drilling of materials such as stone, ceramics, glass, etc.
Diamond grinding fluid/polishing paste: widely used in ultra-precision processing in the electronics, optics, mold and other industries.
Composite diamond material (PCD/PCBN): combines diamond with metal or ceramic matrix to form a composite tool material with toughness and wear resistance.
Ⅱ. Application fields of diamond abrasives
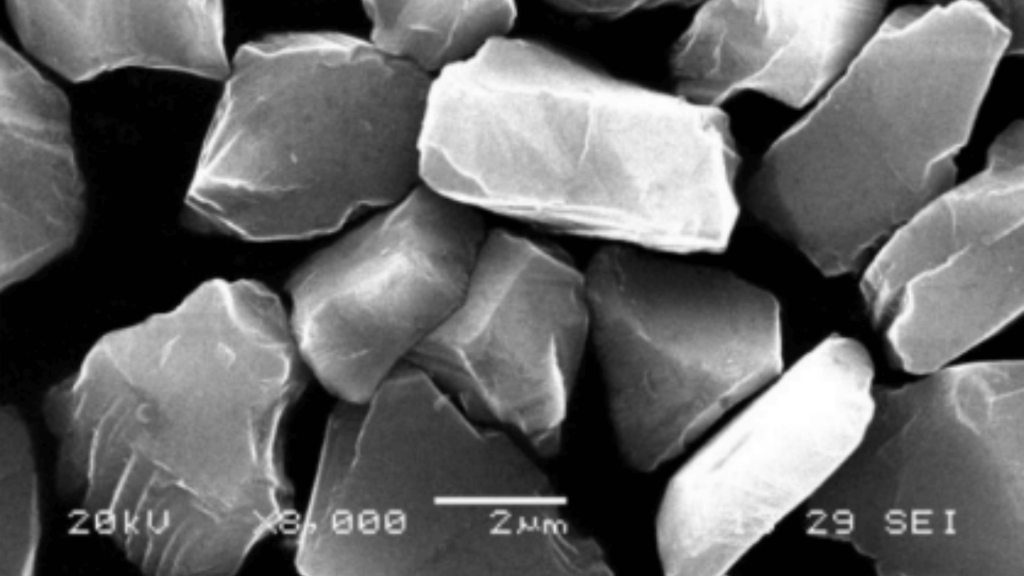 1. Mechanical processingDiamond abrasives are widely used in the shaping and grinding of high-hardness materials, such as cemented carbide, ceramics, silicon carbide, glass, ferrite, etc. Using diamond grinding wheels for processing can not only significantly improve processing efficiency and surface quality, but also extend tool life and reduce tool change frequency. It is particularly suitable for mass-produced, automated high-precision manufacturing processes.
2. Electronics and semiconductor industriesDuring the processing of materials such as silicon wafers, sapphire substrates, silicon carbide chips, optoelectronic glass, etc., diamond wire saws, grinding fluids and polishing pastes are key consumables. Diamond abrasives can achieve submicron or even nanometer-level flatness and roughness. They are widely used in key links such as chip dicing, wafer grinding, and photomask polishing. They are an important factor in ensuring the high performance and high yield of electronic products.
3. Optical processingDiamond powder is widely used in the polishing of optical glass, laser windows, sapphire elements and other components. Its excellent cutting force and chemical stability can effectively improve the quality of mirror processing and achieve a surface roughness Ra of less than 10nm. It is an important material for achieving ultra-smooth surfaces and high light transmittance.
4. Construction and stone processingDiamond saw blades, drill bits, cutting wires, etc. are widely used in the processing of building materials such as granite, marble, and concrete. Compared with traditional tools, diamond tools are superior in cutting speed, service life, and cutting quality, and are particularly suitable for efficient processing of high-strength and high-density building materials.
5. New energy and aerospace
With the development of new energy technology, the demand for diamond abrasives in the processing of lithium battery pole pieces, ceramic diaphragms, electric vehicle components, etc. is growing rapidly. In the field of aerospace, diamond tools are used for precision machining of engine hot end components, composite structural parts, etc., which improves the reliability and durability of products.
1. Mechanical processingDiamond abrasives are widely used in the shaping and grinding of high-hardness materials, such as cemented carbide, ceramics, silicon carbide, glass, ferrite, etc. Using diamond grinding wheels for processing can not only significantly improve processing efficiency and surface quality, but also extend tool life and reduce tool change frequency. It is particularly suitable for mass-produced, automated high-precision manufacturing processes.
2. Electronics and semiconductor industriesDuring the processing of materials such as silicon wafers, sapphire substrates, silicon carbide chips, optoelectronic glass, etc., diamond wire saws, grinding fluids and polishing pastes are key consumables. Diamond abrasives can achieve submicron or even nanometer-level flatness and roughness. They are widely used in key links such as chip dicing, wafer grinding, and photomask polishing. They are an important factor in ensuring the high performance and high yield of electronic products.
3. Optical processingDiamond powder is widely used in the polishing of optical glass, laser windows, sapphire elements and other components. Its excellent cutting force and chemical stability can effectively improve the quality of mirror processing and achieve a surface roughness Ra of less than 10nm. It is an important material for achieving ultra-smooth surfaces and high light transmittance.
4. Construction and stone processingDiamond saw blades, drill bits, cutting wires, etc. are widely used in the processing of building materials such as granite, marble, and concrete. Compared with traditional tools, diamond tools are superior in cutting speed, service life, and cutting quality, and are particularly suitable for efficient processing of high-strength and high-density building materials.
5. New energy and aerospace
With the development of new energy technology, the demand for diamond abrasives in the processing of lithium battery pole pieces, ceramic diaphragms, electric vehicle components, etc. is growing rapidly. In the field of aerospace, diamond tools are used for precision machining of engine hot end components, composite structural parts, etc., which improves the reliability and durability of products.
III. Conclusion
Diamond abrasives, as an important basic material for modern industrial manufacturing, are being adopted by more and more high-precision machining scenarios due to their excellent physical properties and wide applicability. In the future, with the continuous advancement of materials science and manufacturing technology, diamond abrasives will continue to develop in a more refined, intelligent and environmentally friendly direction, helping the high-end manufacturing industry to move to a higher level.
 1. Mechanical processing
1. Mechanical processing